Disclaimer
While APRA endeavours to ensure the quality of this publication, APRA does not accept any responsibility for the accuracy, completeness or currency of the material included in this publication, and will not be liable for any loss or damage arising out of any use of, or reliance on, this publication.
Important notice
The Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics report contains detailed profile and structure, financial performance and financial position, conditions of release, fees and membership information for APRA-regulated superannuation funds with more than four members and eligible rollover funds, as well as profile and structure information for the trustees of these superannuation funds.
Information on rate of return (ROR)
The Annual Fund-level superannuation statistics contains one, five and ten year RORs. ROR is calculated as net earnings after tax over cash flow adjusted net assets. Five and ten year RORs are calculated as the geometric average of the one year RORs for the most recent five and ten year periods. The one year RORs for all periods are available in Table 3 of the back series version of the Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics. For example, the five year annualised rate of return is calculated as:
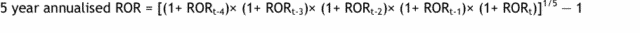
Further information on the calculation of ROR can be found in the Explanatory notes below.
The rate of return (ROR) represents the net earnings on superannuation assets and measures the combined earnings of a superannuation fund’s assets across all its products and investment options. Many trustees provide individual members with the choice of a wide range of investment options and superannuation products, with different investment goals. APRA’s statistics are not designed to provide individual members with information to compare the investment options offered. The Australian Securities and Investments Commission’s MoneySmart website (www.moneysmart.gov.au) provides guidance on how to compare superannuation investment options and links to other sources of information for this purpose. Further, different funds have significantly different proportions of members that use the investment options that are made available by trustees. This can materially affect the overall ROR on superannuation assets for a fund and limits the comparability of the ROR between funds.
Fund year-ends
Most superannuation funds have a year-end of 30 June, however, there are a number of superannuation funds with year-ends other than 30 June. The applicable year-end is noted in the column headed ‘RSE balance date’. Comparisons of returns between superannuation funds with different year-ends should not be made as funds may have experienced different investment market conditions over their respective years of income. Further, in some instances such as when an RSE’s balance date changed during the reference period, the report does not contain 12 months of performance information. The column headed ‘Duration’ indicates the number of months of performance information included in the report. Comparisons of performance between funds with differing durations should not be made.
Explanatory notes
Changes in reporting framework
APRA released a new reporting framework in June 2013. For most RSEs, the first annual forms applied from the year ending 30 June 2014, however detailed membership information was collected for the first time for 2015. Table 3 Fund-level financial performance in the back series version therefore contains information collected under two reporting frameworks. From 2004 to 2013, data was collected under the previous reporting framework, and from 2014 onwards data was collected under the revised reporting framework.
Source of data
Data in the Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics report have been sourced from the following superannuation reporting forms submitted to APRA under the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001 by RSE licensees:
- SRF 001.0 Profile and Structure (Baseline)
- SRF 200.0 Statement of Financial Performance (prior to 1 July 2013)
- SRF 210.0 Statement of Financial Position (prior to 1 July 2013)
- SRF 320.0 Statement of Financial Position (1 July 2013 onward)
- SRF 330.0 Statement of Financial Performance (1 July 2013 onward)
- SRF 410.0 Accrued Default Amounts
- SRF 530.0 Investments (1 July 2014 onward)
- SRF 530.1 Investments (1 July 2013 to 30 June 2014)
- SRF 540.0 Fees • SRF 600.0 Profile and Structure (RSE Licensee)
- SRF 601.0 Profile and Structure (RSE)
- SRF 610.0 Membership Profile (1 July 2014 onward)
- SRF 610.1 Changes in Membership Profile (1 July 2014 onward)
- SRF 710.0 Conditions of Release
The reporting forms, and associated reporting instructions, are available on the APRA website. RSE licensees, RSE names and ABNs used in the report are consistent with the register of RSE licensees and RSEs on APRA’s website and are current at the time of publishing.
Background
On 28 May 2015, APRA released a discussion paper on proposed changes to its annual superannuation statistics and confidentiality of superannuation data. This consultation followed the implementation of revised reporting requirements, which commenced progressively from 1 July 2013, and replaced reporting requirements that had been in place since 2004.
In February 2016, APRA released a response to submissions on the proposed changes to its annual superannuation statistics, as well as the first editions of the revised annual superannuation publications including the Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics.
Population
Superannuation funds included in this report represent the vast majority of superannuation assets regulated by APRA. It contains data for all APRA-regulated superannuation funds with more than four members. Pooled superannuation trusts (PSTs) have been excluded from the publication publications as their assets are captured in other superannuation funds.
Exempt public sector superannuation schemes (EPSSS) have also been excluded. Superannuation funds that wound up during their year of income in a given reference period are not included in that year or subsequent years. Superannuation funds that wound up after the reporting period but before the release of the publication are included for that reporting period, and their wind-up date is noted in the report. Superannuation funds that did not submit an annual return for a given reporting period are not included in that year.
Data items not published
To protect the privacy of individual members, APRA has masked certain items in the publication. Where data have been masked to maintain member privacy this is highlighted with an ‘ * ‘. Items which are blank indicate that either nothing was reported for the relevant period or that the data cannot be calculated.
Information on fund type
The Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics report includes fund type information for each superannuation fund. Details are available in the paper Segmentation of superannuation entities here.
RSE licensee and RSE balance dates
Trustee-level profile and structure information in Table 1 is presented for the year end of the RSE licensee, which is noted in the column headed ‘RSE licensee balance date’. The remainder of the report contains fund-level information presented for the year end of the fund, which is noted in the column headed ‘RSE balance date’. If an RSE’s balance date changes during the reference period, the RSE may submit two annual returns (one standard return and one short return) or may submit one long annual return (greater than 12 months duration). Should the RSE submit two annual returns, the current edition includes only the latest annual return, and the back series edition includes both annual returns as separate rows in the report. The column headed ‘RSE balance date’ indicates the year end of each annual return and the column headed ‘Duration’ indicates the number of months of performance information included in the annual return.
One year rate of return (ROR)
ROR is calculated as net earnings after tax over cash flow adjusted net assets. ROR is only calculated for funds where the data covers a complete 12 months and net assets are non-negligible. The ROR definition assumes that net flows over the year are uniformly distributed. There may be certain occasions when this is not an appropriate assumption. For example, where two funds have merged during the year and there is a large rollover of assets, the timing of this flow may reduce the accuracy of the ROR in measuring performance. In instances where a fund has unusually large rollovers, further information is sought and an adjustment made to net flows to remove the distortion caused by this cash flow. Net flows was not adjusted for any funds in the 2017 Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics report. There may also be limited circumstances where constrained whole-of-fund performance may be expected from a trustee due to the particular circumstances of the superannuation fund. For example, where a superannuation fund is winding up and expects sustained net outflows of funds and members, the trustee may implement an investment strategy with a higher weighting to more stable and liquid assets which will generally earn a lower rate of return. Additionally there are some superannuation funds with very large negative rates of return, these are caused by the structure of the funds as they only operate for insurance purposes.
Five and ten year ROR
Five and ten year RORs are calculated as the geometric average of the one year RORs for the most recent five and ten year periods. The one year RORs are available in Table 3 of the back series version of the Annual Fund-level Superannuation Statistics. For example, the five year annualised rate of return is calculated as:
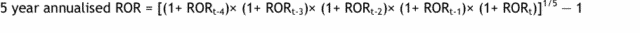
where t equals the current year-end.
Five and ten year RORs are blank when an insufficient number of years of performance information are available, or when the return is unable to be published as a meaningful statistic. If an entity’s balance date changes during the five or ten year period and the rate of return is for a non-standard length, then the period of the return is footnoted.
Information on fees, expenses and taxes
Information on fees, expenses and taxes included in this publication should be used for indicative purposes only. Information may reflect inconsistencies in reporting that should be considered when using the data provided. Expenses are generally understated within this publication for the following reasons: • indirect investment expenses are generally not reported as this information is not separately identifiable in most cases; • not all entities are able to provide complete information; and • data collected may not adequately capture some expenses. Entities also adopt different approaches to recognise future tax liabilities and assets.
Glossary
| Account closure: Consolidation of accounts represents a member account closed where all benefits in that account have been consolidated with another account of the same member in the same RSE. |
| Account closure: Outward rollover represents a member account closed where all benefits in that account have been rolled out/transferred to another RSE. Exclude: rollovers due to successor fund transfers. Reference: SIS Regulation, r. 1.03. |
| Account closure: Satisfying a condition of release represents a member account closed where all benefits in that account have been paid to a beneficiary where a condition of release within the meaning given in Schedule 1 of the SIS Regulations is satisfied. |
| Account closure: Successor fund transfer represents a member account closed where a member’s benefit is transferred without the member’s consent from one RSE to a successor fund within the meaning given in r. 1.03 of the SIS Regulations. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 6.29. |
| Accrued default amounts (ADA) represents the total amount attributed by the trustee to a member is defined as an accrued default amount in section 20B of the SIS Act where either the member has given the trustee of the fund no direction on the investment option in which the amount is to be invested; or the investment option in which the total amount is invested in is one which, under the current governing rules of the fund, would be the investment option for a new member if no direction were given. |
| Active member account represents a member account that has received contributions, rollovers, or transfers or has made benefit payments within the last two years and which has not been closed. Excludes: lost member accounts and inactive member accounts. |
| Activity fee represents a fee charged to a member that relates to an activity of an RSE licensee that is engaged in at the request of, or with the consent of, a member or that relates to a member and is required by law. |
| Administration expenses represents expenses that relate to the administration or operation of the fund. Includes: administration expenses for which administration fees are charged. Report the total expense charged by an administrator where the administrator is also a service provider of activities other than administration e.g. custodial, and the expense is not segregated by activity type. |
| Administration fee represents a fee charged to a member that relates to the administration or operation of the fund. |
| Advertising/marketing represents activities associated with the promotion or delivery of goods or services, brand or entity. Includes: promotion and sponsorship activities. |
| Advice expenses represents expenses that relate to the provision of financial product advice to a member. Includes: expenses for which activity fees relating to provision of financial product are charged. |
| Advice fee represents a fee charged to a member that relates to the provision of financial product advice to a member by the RSE licensee. |
| Age bracket represents a segmentation of data based on the age of the member in years. |
| Age not available represents where the date of birth of a member is not known. |
| Attaining age 65 condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the attaining age 65 condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Attaining preservation age condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the attaining preservation age condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Average remuneration represents total director remuneration of directors on trustee board over total number of directors on trustee board. |
| Benefit payments represents lump sum benefit payments and pension benefits paid directly to members. Excludes: rollovers and successor fund transfers. Reference: SIS Regulations, Divisions 6.2 and 6.3; Superannuation Industry (Unclaimed Money and Lost Members) Act 1999, Part 4A. |
| Cash flow adjusted net assets is the sum of net assets at the beginning of the period and half of the sum of net members’ benefit flows and net insurance flows. |
| Cash represents cash on hand and demand deposits, as well as cash equivalents. Cash equivalents represent short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Commissions represents compensation for the facilitation of a transaction, such as buying or selling a particular product. Includes: commissions to brokers, agents, advisers, salespersons. |
| Commodities represents natural resources that are either grown or extracted from the ground and are often used as inputs in the production of other goods or services. |
| Compassionate grounds condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the compassionate grounds condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Contributions tax and surcharge represents tax expenses in relation to taxable contributions made to the superannuation entity during the period (contributions tax) and contributions surcharge tax. |
| Corporate base represents where members join the RSE as a result of working for a single employer-sponsor, or an associate of the employer-sponsor, of the RSE. Reference: SIS Act, s. 16(1). |
| Corporate funds are RSEs with more than four members under the trusteeship of a ‘not for profit’ RSE licensee and with a corporate membership base. |
| Custodian represents the person or entity that performs custodial functions in relation to any of the assets of the RSE. Reference: SIS Act, s. 10(1). |
| Death condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the death condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Defined benefit contribution represents contributions made in respect of a member interest that is a defined benefit interest. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 1.03AA. |
| Defined benefit interests represents a member interest that is a defined benefit interest or a defined benefit pension. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 1.03AA, r. 9.04E. |
| Defined benefit members’ benefits represents the present value of expected future benefit payments to defined benefit members and beneficiaries arising from membership, measured using actuarial assumptions and valuations where appropriate. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Defined contribution interests represents a member’s interest in an RSE that is not a defined benefit interest. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 1.03. |
| Defined contribution members’ benefits represents the present obligation to pay benefits to defined contribution members and beneficiaries. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Director represents a director of an RSE licensee, within the meaning given in s. 10(1) of the SIS Act. A reference to ‘a director’ is, in the case of a group of individual trustees, an individual trustee. |
| Director remuneration represents remuneration paid to a director, individual trustee or alternate director of the RSE licensee with respect to their role for the RSE licensee, where remuneration has the meaning given, in the context of an officer (including an RSE licensee director), in the Part 9 Dictionary of the Corporations Act 2001. Reference: Corporations Act 2001, s. 201K; Prudential Standard SPS 510 Governance. |
| Directors on trustee board includes directors, individual trustees and alternate directors. |
| Directly held represents investments made by the RSE in its own name. Includes: investments held by a custodian in trust for the RSE. |
| Director/individual trustee expenses represents compensation to a director for services provided in carrying out the functions of a director, including but not limited to non-compliance related consulting or administration services. Excludes: amounts paid to a director for reimbursement of expenses, professional indemnity insurance costs; commissions collected for payment to a third party. |
| Dividend revenue represents gross revenue in the form of dividends. |
| Employer contribution represents contributions made by an employer on behalf of the member. Includes: employer contributions made to an accumulation account on behalf of members to meet super guarantee, award or other obligations, contributions paid as a result of a salary sacrifice arrangement, transfers from consolidated revenue funds for EPSSSs and constitutionally protected funds, and super guarantee charge and the taxable component of any super holding accounts special account amounts which the ATO transferred to the provider on behalf of the member. Reference: Member Contribution Statement. |
| Employer-sponsor (non-public sector) ownership represents where the owner of the RSE licensee is the principal employer-sponsor of an RSE within the RSE licensee’s business operations. Include: where the RSE licensee is owned by employees of the employer-sponsor. Reference: SIS Act, s. 16(1). Exclude: where the employer-sponsor is a public sector organisation. |
| Equal representation required by governing rules represents where the RSE licensee chooses to have an equal-representation board structure. Reference: SIS Act, s. 89. |
| Equal representation required by legislation represents where the RSE licensee is required to have an equal-representation board structure. Reference: SIS Act, s. 89. |
| Equity represents an ownership interest in a business, trust or partnership. Includes: common shares, preference shares and units. Excludes: units in property trusts, units in infrastructure trusts. |
| Excess contributions tax (ECT) release conditions of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the Excess contributions tax (ECT) release condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Exit fee represents a fee charged to a member to recover the costs of disposing of all or part of members’ interests in a fund. |
| Fee discount represents a discount applied against fees charged to members. |
| Fee paid by employer sponsor represents where the employer-sponsor, within the meaning given in s.16(1) of the SIS Act, pays the fee. Include: fees paid by way of an employer contribution that has not been allocated to member accounts, and, fees paid directly by an employer to a service provider without passing through the RSE. |
| Fee paid by member represents where the fee charged to the member has been paid directly either as a deduction from the member’s account, member’s contributions or from the investment return before crediting the member’s account balance. |
| Fee paid by reserve represents where the fee is paid from a reserve with the RSE. |
| Fee paid by RSE licensee represents where the RSE licensee pays the fee, either as a payment into the RSE by the RSE licensee or directly by the RSE licensee to a service provider without passing through the RSE. |
| Fee rebate represents a rebate received against fees charged to members. |
| Financial services corporation ownership represents where the owner of the RSE licensee is a financial services corporation, i.e. the owner is a legal entity created for the purpose of producing financial goods and services for the market, that may be a source of profit or other financial gain to its owner(s) and it is collectively owned by shareholders who have the authority to appoint directors responsible for its general management. Excludes: a financial services corporation that is the principal employer-sponsor of all RSEs within the RSE licensee’s business operations. |
| Fixed Income represents a loan, placement or debt security. Loans are financial assets that are created when a creditor lends funds directly to a debtor, and are evidenced by documents that are non-negotiable. Placements are liabilities of entities not described as authorised deposit-taking institutions, e.g. State treasuries. Debt securities are securities which represent borrowed funds which must be repaid by the issuer with defined terms including the notional amount (amount borrowed), an identifiable return and maturity/renewal date. Includes: short and long-term debt securities. |
| For profit status represents where an RSE licensee cannot be classified as being not for profit status. |
| General base represents where the predominant base of members of the RSE cannot otherwise be categorised as government base, corporate base and industry base. |
| Government base represents where members join the fund as a result of working for a government organisation, including quasi-corporations controlled by the general government sector. A government organisation is a legal entity established by political processes that have legislative, judicial or executive authority over other institutional units in a given area; are financed mainly from taxation or government transfers; and are principally involved in the provision of goods and services free of charge or at economically insignificant prices. |
| Government co-contribution represents contributions made by the Federal Government to the RSE under the Superannuation (Government Co-Contribution for Low Income Earners) Act 2003. |
| Impairment expense represents the change in the cumulative provision for impairment charges, relating to total investment income. An impairment loss is the amount by which the carrying amount of an asset or a cash-generating unit exceeds its recoverable amount i.e. represents the portion of total investment income/distributions that the RSE no longer considers probable to collect. |
| Inactive member account represents a member account that has not received any contributions, rollovers or transfers, or made any benefit payments within the last two years but which has not been closed as the member is contactable. Includes: members that joined an RSE, as a standard employer-sponsored member, more than two years ago and there have been no contributions or rollover amounts in respect of that member within the past five years. Excludes: lost member accounts and active member accounts. |
| Industry base represents where members join the RSE as a result of working in a particular industry sector. |
| Industry funds are RSEs with more than four members under the trusteeship of a ‘not for profit’ RSE licensee and with either an industry or general membership base. |
| Infrastructure represents the basic physical systems of a country, state or region including transportation, communication, utilities, and public institutions. |
| Insurance fee represents a fee charged to a member that relates directly to insurance premiums paid by the RSE licensee in relation to a member or members. Excludes: insurance contracts where the benefit to the member is based on the performance of an investment rather than the realisation of a risk. |
| Interest revenue represents gross revenue in the form of interest. |
| Intrafund advice represents financial product advice to members within the meaning given in s. 99F of the SIS Act. |
| Investment consultant represents a person engaged to provide investment advice. Includes: asset consultants and implemented consultants. |
| Investment expense ratio represents total investment expenses over cash flow adjusted net assets. |
| Investment expenses represents expenses that relate to the investment of the assets of the entity. Includes: expenses for which investment fees are charged and expenses associated with generating income on investments. |
| Investment fee represents a fee charged to a member that relates to the investment of the assets of the entity. |
| Investment income and gains/losses represents the total investment income from superannuation activities. Includes: investment income after impairment expense, gains/losses on investments and other investment income. |
| Investment income represents gross revenue in the form of income or distributions from investments. Includes: interest, dividends, rental income, trust distributions. |
| Investment management base fee represents investment fees which are not determined by reference to the performance of the investments made by the investment manager on behalf of the RSE licensee of an RSE. Excludes: investment management performance based fees. |
| Investment management performance based fee represents investment fees which are determined, in whole or in part, by reference to the performance of an investment made by an investment manager on behalf of the RSE licensee of an RSE. Includes: accrued performance fees, past loss clawbacks in performance fees. Excludes: investment management base fees. |
| Investment option represents, at a minimum, pre-mixed options, investment vehicles and instruments that are made available, or have previously been made available, by the RSE licensee from which members of an RSE can select when determining how their interest is to be invested. |
| Inward rollovers represents rollovers and successor fund transfers into the fund. |
| Inward insurance flows represents inflows sourced from insurance activities. Includes: insurance claim benefits or proceeds credited to member accounts, reinsurance benefits, rebate income received on premiums charged, fee rebates received against insurance fees charged to members and changes in insurance liabilities or reinsurance assets. |
| Lost member account represents the account of a member who is inactive and is uncontactable or who transferred from another RSE as a lost member. Excludes: members that have confirmed their address in the past two years, members that have indicated that they want to remain a member, inactive member accounts and active member accounts. Reference: SIS Regulations r. 1.03A |
| Lost member who is found condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the lost member condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1, Item 111. |
| Low income super contribution represents contributions made by the Federal Government to the RSE for an individual member within the purposes of the Tax Laws Amendment (Stronger, Fairer, Simpler and Other Measures) Bill 2011. |
| Lump sum benefit payment represents benefit payments that have been paid as a lump sum under a condition of release, from pooled superannuation trust arrangements or classed as another benefit payment type. Includes: insurance claim benefits or proceeds first credited to members’ accounts and subsequently disbursed along with members’ benefits to the member or beneficiary as a lump sum benefit payment. Reference: SIS Regulations, Schedule 2. |
| Member account represents a distinct entry recorded in the register of member accounts (or other equivalent mechanism). |
| Member account without a TFN represents a member account for which the RSE does not have a tax file number recorded to identify the member. |
| Member account with a TFN represents a member account for which the RSE has the member’s tax file number recorded to identify the member. |
| Member contributions represents contributions made by a member including non excluded capital gains or capital proceeds and personal injury payments, direct termination payments, other third party contributions (low income superannuation contributions, government co-contributions and other family and friend contributions) and other contributions made by a person other than the employer. Reference: Member Contribution Statement. |
| Member initiated activity represents an activity that is engaged in at the request, or with the consent, of a member. Excludes: an activity that relates to a member and is required by law. |
| Members’ benefit bracket represents a segmentation of data based on the liability for member benefits owing to defined contribution members and defined benefit members. Excludes: unallocated contributions. |
| Members’ benefit flows represents members’ monies paid into or out of the entity. |
| Membership base represents the classification of the predominant base of members within the RSE. Predominant base means more than half of the overall fund membership. |
| MySuper product refers to a class of beneficial interest in a regulated superannuation fund that is a MySuper product if an RSE licensee is authorised under section 29T (including section 29TA and 29TB) to offer that class of beneficial interest in the fund as a MySuper product. |
| Net after tax contributions represents the sum of employer contributions, member contributions and defined benefit contributions less contributions tax and surcharge. |
| Net assets represents the surplus of total assets less total liabilities which is underlying the value of members’ benefits. Includes: reserves. |
| Net earnings after tax are net earnings generated during the period less tax expense on earnings. |
| Net earnings are the sum of net investment income and other income less operating expenses. |
| Net insurance flows is used in the calculation of rate of return. It represents inward insurance flows less outward insurance flows. |
| Net members’ benefits flows is used in the calculation of rate of return. It represents total members’ benefit flows in plus net rollovers less total members’ benefit flows out. |
| Net members’ benefit outflow ratio represents the sum of total members’ benefits flows out and outward rollovers over the sum of total members’ benefits flows in and inward rollovers. |
| Net rollovers is the difference between inward rollovers and outward rollovers. |
| New member account: Employer sponsor represents a member account created where the member’s employer is an employer sponsor of the fund. Reference: SIS Act, s. 16(1). |
| New member account: Member, tax free phase represents a member account created where the member has elected to set up a tax free phase member account and, that is not associated with the member’s employer. Tax free phase represents where the members’ benefits are no longer liable for income tax due to the member being eligible to access his or her superannuation. Includes: transition to retirement member accounts. |
| New member account: Member, taxed phase represents a member account created where the member has elected to set up a taxed phase member account and, that is not associated with the member’s employer. Taxed phase represents where the members’ benefits are liable for income tax due to the member being ineligible to access his or her superannuation. |
| Nominating organisation ownership represents where the owner of the RSE licensee is an employee association or employer association that represents the membership/employers of the RSEs within the RSE licensee’s business operations. Includes: where the RSE licensee is owned by directors representing the membership/employers of the RSEs within the RSE licensee’s business operations. |
| Non-equal representation represents where the RSE licensee does not maintain any form of equal representation on the Board. |
| Not for profit status represents where the RSE licensee’s business operations are not a source of income, profit or other financial gain to the RSE licensee owners, or associates of the RSE licensee owners, that establish, control or finance the legal entity. |
| Operating expense ratio represents total administration and operating expenses over cash flow adjusted net assets. |
| Operating expenses represents expenses that relate to the operation of the fund by the RSE licensee. Includes: operating expenses for which administration fees are charged, such as expenses relating to advertising/marketing, commissions, director/individual trustee expenses, operating expenses associated with service provider and other operating expenses. Excludes: administration expenses. |
| Operating income represents income sourced from miscellaneous operating activities. Includes: income from scrip lending; income associated with underwriting activities; fees and commissions; rebates on fees charged to members, costs, commissions and charges; and other miscellaneous income. Excludes: investment income. |
| Other investments include all investments not separately disclosed in the specified investment categories. |
| Other members’ benefits flows in represents total members’ benefit flows into the RSE minus the sum of net after tax contributions, rollovers, successor fund transfers and units issued. |
| Other members’ benefits flows out represents total members’ benefit flows out of the RSE minus the sum of benefit payments, rollovers out of the RSE, successor fund transfers out of the RSE, repatriation to employer sponsor and payments to unit holders. |
| Outward insurance flows represents outflows incurred through insurance activities. Includes: premiums debited from member accounts, reinsurance premiums charged, expenses incurred for insurance claims and changes in insurance liabilities or reinsurance assets. |
| Outward rollovers represents rollovers and successor fund transfers out of the fund. |
| Payments to unit holders represents payments from pooled superannuation trusts (PSTs) to unit holders of those PSTs. Excludes: rollovers paid out on behalf of unit holders. Reference: SIS Act, s. 10. |
| Pension benefit account represents the member account or portion thereof, from which pension benefit payments are payable under a condition of release. Includes: complying pensions, allocated pensions, annuity payments and payments from longevity products/variable annuities. Excludes: amounts resulting from the commutation of pension benefits. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 1.05 and r. 1.06. |
| Pension benefit payment represents benefit payments that have been paid as a pension under a condition of release. Includes: account based pension, transition to retirement pension, allocated pensions, annuity payments and other pension income streams. Excludes: transfers, including rollovers and successor fund transfers, within the superannuation system. Reference: SIS Regulations, Divisions 6.2 and 6.3. |
| Permanent incapacity condition or release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the permanent incapacity condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Personal contribution represents contributions made by a member as defined in the Member Contribution Statement, Includes: contributions which have counted toward the non-concessional and concessional contributions cap, non excluded capital gains or capital proceeds and personal injury payments, direct termination payments and contributions from another entity on the members behalf, CGT personal injury exclusions, DTPs (made by a member to an account in their own name including both deducted and non-deducted member contributions). |
| Property represents an investment in real estate where the earnings and capital value are dependent on cash flows generated by the property through sale or rental income. |
| Proportion of benefits which are defined benefits represents defined benefit interests as a percentage of the sum of defined benefit and defined contribution interests. |
| Proportion of total assets in default or MySuper Strategy represents accrued default amounts and MySuper assets as a percentage of the fund’s total assets. |
| Public company ownership represents where the owner of the RSE licensee is a public company. Excludes: a public company that is a financial services corporation, a public company that is the principal employer-sponsor of an RSE. |
| Public sector funds are RSEs with more than four members under the trusteeship of a ‘not for profit’ RSE licensee and with a government base membership base. Public sector funds also include superannuation schemes established by a Commonwealth, State or Territory law (known as exempt public sector superannuation schemes). |
| Public sector organisation ownership represents where the owner of the RSE licensee is an organisation within the government sector or a resident corporation and quasi-corporation controlled by the general government sector. Includes: where the public sector organisation is the principal employer-sponsor of an RSE within the RSE licensee’s business operations. |
| Rate of return is net earnings after tax divided by cash flow adjusted net assets. |
| Realised gains/losses represents changes in the value of investments as a result of closing or disposal of investments. |
| Rental income represents gross revenue in the form of rental income from property investments. |
| Repatriation to employer sponsor represents where member benefits are paid back to employer sponsors that were originally received from employer sponsors either in the form of contributions or amounts associated with the redemption of fund assets. Excludes: amounts paid back to employer sponsors that relate to services provided, such as administrator fees. Reference: SIS Act, s. 117. |
| Retail funds are RSEs with more than four members under the trusteeship of a ‘for profit’ RSE licensee with a corporate, industry or general membership base. |
| Retail – ERF funds are eligible rollover funds under the trusteeship of a ‘for profit’ RSE licensee with a corporate, industry or general membership base. |
| Retirement condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the retirement condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Rollover represents an amount that is transferred between superannuation funds, approved deposit funds, deferred annuities or retirement savings accounts. Excludes: successor fund transfers. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 5.01, r. 6.28 and 6.29. |
| RSE licensee refers to a constitutional corporation, body corporate or group of individual trustees that holds an RSE licence granted under s. 29D of the SIS Act. |
| RSE means a registrable superannuation entity as defined in section 10(1) of the SIS Act. |
| Salary sacrifice contribution represents contributions via an arrangement under which an employee agrees to forego part of his or her total remuneration that he or she would otherwise expect to receive as salary or wages, in return for the employer, or an associate of the employer, providing contribution benefits of a similar value. Reference: Taxation Ruling 2001/10, paragraph 19. |
| Service provider represents an entity or individual that provides any type of service to the RSE licensee to assist or support the RSE licensee in carrying out its duties as an RSE licensee. Includes: accountant, administrator, asset consultant, custodian, financial advisor: employer, financial advisor: member, implemented consultant, professional indemnity insurer, internal auditor, investment manager, IT service provider, lawyer, platform provider, promoter, RSE actuary and RSE auditor. |
| Severe financial hardship condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the severe financial hardship condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| SMSF rollover represents a rollover associated with a self managed superannuation fund. |
| Successor fund transfer represents a transfer of a member’s benefits without the member’s consent from one RSE to a successor fund within the meaning given in r. 1.03 of the SIS Regulations. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 6.29. |
| Super guarantee contribution represents contributions made by an employer to the RSE to meet its obligations under the Superannuation Guarantee (Administration) Act 1992. Includes: defined contribution employers’ contributions. Excludes: defined benefit contributions. Reference: SIS Regulations, r. 1.03. |
| Surplus/deficit in net assets represents the excess/deficiency in net assets available for members’ benefits against total liability for members’ benefits. Excludes: reserves, unallocated contributions. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Switching fee represents a fee charged to a member to recover costs of switching all or part of members’ interests within the fund. |
| Tax free phase represents where the members’ benefits are no longer liable for income tax due to the member being eligible to access his or her superannuation. |
| Taxed phase represents where the members’ benefits account are liable for income tax due to the member being ineligible to access his or her superannuation. |
| Temporary incapacity condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the temporary incapacity condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Terminal medical condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the terminal medical condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. |
| Termination condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the termination condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1. Excludes: rollovers following a termination event and termination with less than $200. |
| Termination with less than $200 condition of release represents benefit payments made to a beneficiary based on satisfaction of the termination of employment with less than $200 condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1, Item 104. Excludes: rollovers following a termination event. |
| Total assets represents resources: (a) controlled by an entity as a result of past events; and (b) from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Total investments represents the purchase of a financial product or other item of value with an expectation of favourable future returns. Excludes: derivative assets, derivative liabilities and property, plant and equipment. |
| Total liabilities represents present obligations of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Total liability for members’ benefits represents the present obligation to members and beneficiaries for benefits they are entitled to receive in the future as a result of membership of the RSE. Excludes: reserves. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Trust distribution represents gross revenue in the form of a trust distribution. |
| Unallocated contributions represents contributions received but not yet allocated to specific member accounts or reserves. Reference: Australian Accounting Standards. |
| Unclaimed money and lost members condition of release represents benefit payments made to the ATO based on satisfaction of the unclaimed money and lost members condition of release, within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Schedule 1, Item 103B and under the Superannuation (Unclaimed Money and Lost Members) Act 1999, Part 4A. |
| Unique TFN represents each distinct tax file number recorded to identify a member, but which may be recorded multiple times across multiple member accounts. |
| Units issued represents contributions received and receivable from pooled superannuation trust unit holders. Reference: SIS Act, s. 48; SIS Act, s. 10. |
| Unrealised gains/losses represents changes in the value of investments as a result of remeasurement changes in the market value of investments. Includes: impairment charges and provisions. |
| Unrestricted non-preserved benefits represents unrestricted non-preserved benefits within the meaning given in SIS Regulations, Subdivision 6.1.4. |